Blog
Pupillary Assessment With Infrared Goggles: A Vestibular Therapist’s Guide
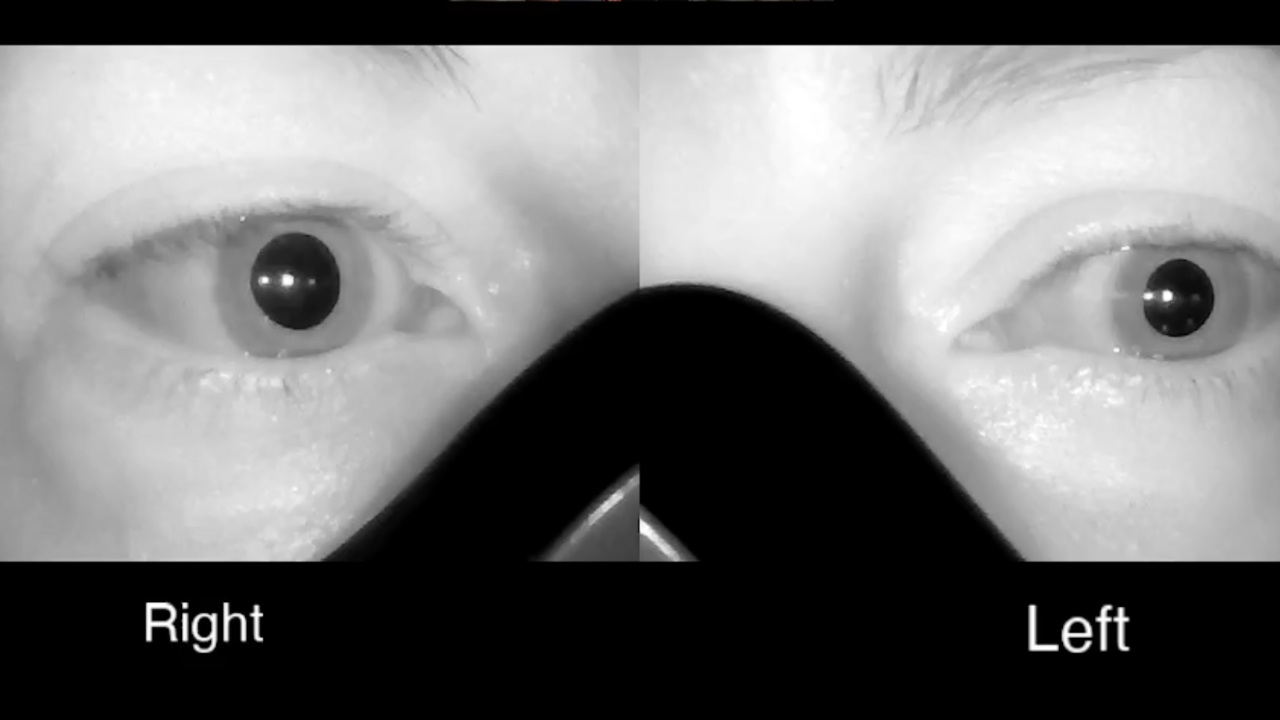
Many vestibular clinicians capture eye movements routinely, but what if your infrared goggles were revealing clues about autonomic nervous system function, not just nystagmus?
A chiropractor friend of mine recently sent me a recording of a patient with atypical positional nystagmus, one of those cases where the eye movements do not follow the usual “BPPV patterns.” We worked through the positional findings and landed on a reasonable clinical interpretation and plan.
My friend who shared the recording is an exceptionally sharp clinician, currently working on his PhD, with deep expertise in the autonomic nervous system. What really caught my attention was his notes stating:
Cranial Nerve...
Exploring the Skull Vibration Induced Nystagmus Test (SVINT)

We’re excited to share an assessment technique that has significantly enhanced our ability to evaluate patients with vestibular hypofunction: the Skull Vibration Induced Nystagmus Test (SVINT). After hearing about it a few times over the past few years, we decided to investigate further and are glad we did. Given our access to infrared goggles, implementing SVINT was quite affordable since portable handheld massage devices can be picked up at places like Walmart.
Clinically, the test has helped us pick up vestibular hypofunctions when our other battery of tests such as looking for gaze evoked nystagmus, head impulse test, head shaking nystagmus test, and dynamic visual acuity tests were unr...
Infrared Goggles: A Comparative Guide for Vestibular Therapists

At North 49, the three common questions we get asked about infrared goggles are:
- Can we get a discount rate on goggles through North 49?
- Do I really need goggles?
- Which goggles do you recommend?
Can we get a discount rate on goggles through North 49?
The answer to the first question is, unfortunately no. That being said, we would really appreciate that if you end up buying a pair of goggles from Vestibular First that you use: https://vestibularfirst.com/?referredby=507 as it allows us to collect points that we redeem to purchase anatomical models that we give out as draws at our weekend courses. From time to time we also have give-away draws for our monthly newsletter subscribers.
...How To Treat Anterior Canal BPPV

With going to vestibular therapy courses have you found that learning how to treat BPPV affecting the anterior canal is often overlooked. This is understandable to some extent given that other vestibular conditions are more prevalent. Specifically with BPPV, according to Bhattacharyya, it only affects the anterior canal up to 3% of the time. Not nearly as common as the other two canals, where much of the training focuses on.
With that being said, BPPV affecting the anterior canal is rare, but it does happen. So, if you are treating patients with dizziness it is just a matter of time until you may see this form of BPPV. When you do it will be good to have a treatment technique up your sleeve...
Ewald's Laws for BPPV & Nystagmus

Ever heard of Ewald's Laws?
If not, with assessing BPPV do you ever wonder why:
- With BPPV affecting the posterior canal, going into the Dix-Hallpike Test is more provocative than sitting up after?
- With BPPV affecting the lateral canal, going into the Supine Roll Test the side that is more provocative is not always the affected side?
- With cupulolithiasis affecting the lateral canal, the nystagmus beats towards the affected ear with the Lean Test?
Maybe you have not, but understanding the WHY behind these will help us treat the atypical forms of BPPV. It will also help us determine if there is another vestibular condition at play, mimicking BPPV.
What are Ewald’s Laws?
There are thr...
Deep Head Hang Maneuver to Treat BPPV

If you are like us, you taken many vestibular therapy courses without being taught how to treat BPPV affecting the anterior canal. Granted, BPPV affecting the anterior canal is rare. If you, however, see a lot of patients with dizziness you will likely see this form of BPPV at some time. When that does occur what are your options?
- Search Dr. Google and hope for the best.
- Ask a colleague.
- Figure it out using an anatomical model (if you have one).
- Hope it will resolve spontaneously.
- Other.
Given such, let's review a treatment option that we have found simple and effective called the Deep Head Hang Maneuver. Before we review the technique let's review some background information.
How...
Thinking About Getting Infrared Goggles, Then This Is A MUST READ
The Dilemma With Getting Infrared Goggles
Are you a busy clinician who has ventured out in the field of vestibular therapy, but find it hard to justify the cost of purchasing infrared goggles? You know they would really help with your assessment, take out some of the guess work, and improve your outcomes. As most things, it can come down to the "budget". Maybe you do not see enough dizzy patients to justify the expense or the owner of the clinic you work at does not understand their value.
Our Journey To Find Infrared Goggles
We get it as we have been there, but fortunately over the years we have been able to gradually purchase infrared goggles. We actually have several sets given our v...
Teasing Out The Torsional Nystagmus with BPPV
Do you ever find it difficult to see the torsional component of nystagmus with the Dix-Hallpike test? At times we have, and it can be concerning given the possibility of the vertical nystagmus being indicative of a central vestibular disorder. There is, however, a clinical trick to help tease out any torsional component.
It's All About Semicircular Canal Orientation
As the video in this blog reviews, the nystagmus with BPPV is in the same plane as the  semicircular canal that is affected. So, with being able to understand the orientation of the canals we can bias the nystagmus to reveal the torsional component and if need be the vertical component.
semicircular canal that is affected. So, with being able to understand the orientation of the canals we can bias the nystagmus to reveal the torsional component and if need be the vertical component.
To see more of the torsional component ...
What Is Nystagmus?
Nystagmus What Does It Mean?
At North 49 our team of vestibular therapists look for nystagmus in determining one’s cause of dizziness. So, what is nystagmus? It is simply repetitive, uncontrolled eye motion. It usually affects both eyes. Depending on the cause it may be constant or intermittent. It can also be temporary or permanent.
Nystagmus how to pronounce?
nuh-stag-muhs
Nystagmus what does it look like?
It will look like a stuttering motion of the eyes. This motion can be linear (upward, downward, or laterally), rotary, or a combination. Sometimes it can be seen in room light while other times it cannot. Health care providers therefore use infrared goggles to make sure that t...


